Leave Your Message
The significance of Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride in contemporary chemical applications cannot be overstated. This compound, characterized by its unique brominated structure, has garnered attention across various industries for its remarkable properties, including flame retardancy and chemical stability. As the demand for safer and more efficient materials grows, Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride emerges as a crucial component in the formulation of polymers, resins, and adhesives that meet stringent safety standards.
In recent years, the versatility of Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride has paved the way for innovation in fields such as electronics, construction, and automotive manufacturing. Its ability to enhance the performance of materials while providing essential fire resistance makes it invaluable in the development of high-performance products. Moreover, the compound's compatibility with a range of substrates adds to its appeal, allowing for widespread utilization in diverse applications.
As industries strive to achieve more sustainable practices while prioritizing safety, Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride stands out as an essential ingredient. Its role in advancing modern chemical formulations, coupled with its eco-friendly attributes, positions it as an integral element in the ongoing evolution of material science. This introduction lays the groundwork for a deeper exploration of how Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride influences contemporary chemical applications and its potential for future advancements.

Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) is a compound with significant relevance in the fields of polymer science and flame retardant technology. Its development can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the increasing need for fire-resistant materials in various industries revealed the shortcomings of existing flame retardants. Researchers sought alternatives that offered enhanced thermal stability and performance, leading to the synthesis of TBPA. Historically, it was recognized for its efficiency in reducing flammability while maintaining the mechanical integrity of materials, which made it a subject of interest in both academic and commercial research.
By the late 1990s, industry reports indicated a marked growth in the adoption of TBPA in various applications, particularly within thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers. A study conducted in 2021 highlighted that the global market demand for TBPA had reached approximately 12,000 metric tons, primarily driven by its application in electronics, textiles, and construction materials. The compound's ability to improve flame resistance without compromising physical properties has made it a staple in the formulation of polyurethane and epoxy resins, offering manufacturers a reliable solution to meet stringent safety regulations. Overall, TBPA's development represents a critical advancement in chemical engineering that aligns with the evolving demands for safety and performance in modern materials.
Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride plays a crucial role in various modern chemical applications across several industries, as illustrated in the graph above. The data highlights its significant usage in electronics, coatings, and other sectors, emphasizing its relevance in contemporary material development.
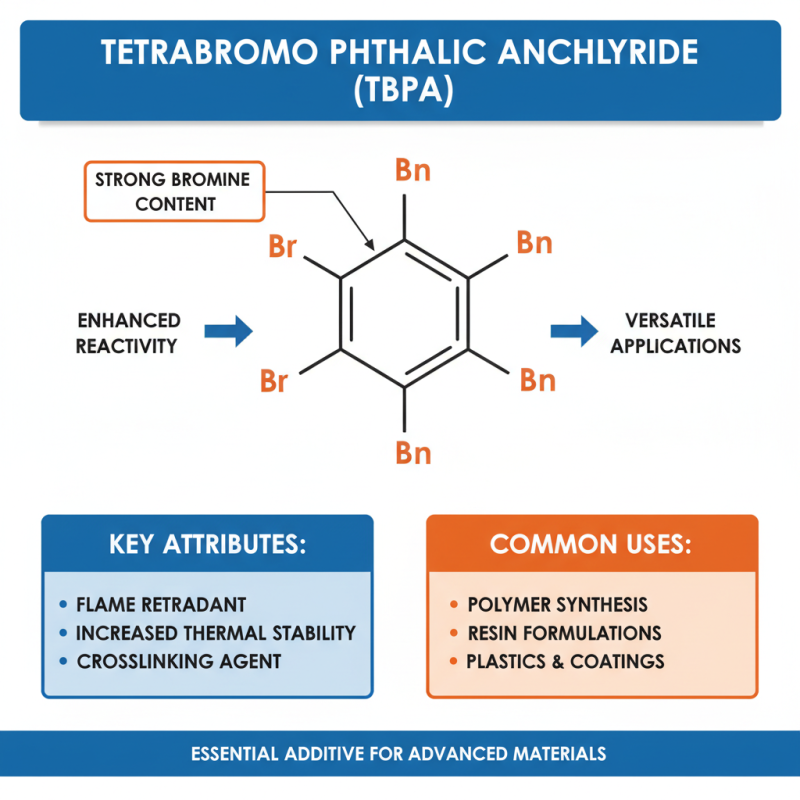
Tetrabromo phthalic anhydride (TBPA) is a compound characterized by its strong bromine content, which significantly enhances its reactivity and versatility in chemical applications. Its chemical structure comprises a phthalic anhydride framework with four bromine atoms substituted on the aromatic rings. This substitution not only increases its thermal stability but also contributes to its effectiveness as a flame retardant. The presence of bromine facilitates the formation of cross-linked structures during polymer synthesis, making TBPA an essential additive in various resin formulations.
The properties of tetrabromo phthalic anhydride also include its ability to engage in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, which can be utilized in creating diverse polymers with unique characteristics. Its high reactivity allows for the incorporation of TBPA into copolymers, enhancing their mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Additionally, TBPA's anhydride functional groups provide sites for further chemical modification, enabling tailored properties for specific applications, such as in coatings, adhesives, and plastics. Overall, the unique chemical structure and properties of tetrabromo phthalic anhydride play a crucial role in modern chemical engineering and material science.
Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) is gaining recognition in various industrial applications due to its unique properties. Primarily used as a flame retardant, TBPA plays a crucial role in enhancing the fire resistance of polymers and resins. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global flame retardant market is projected to reach $11.8 billion by 2025, with TBPA being a significant contributor, especially in industries like construction, automotive, and electronics. The compound effectively reduces the flammability of materials, extending their lifespan and improving safety standards.
Furthermore, TBPA finds applications in the manufacturing of specialty coatings and adhesives. Its ability to provide thermal stability and chemical resistance makes it ideal for protective coatings used in industrial environments. A recent study published by TechSci Research highlighted that the coatings segment is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2022 to 2027, driven largely by the demand for high-performance materials, where TBPA is increasingly incorporated due to its beneficial properties.
Tips: When considering the use of TBPA in manufacturing processes, it is essential to conduct thorough compatibility tests with other materials to optimize performance. Additionally, staying updated on regulatory guidelines can help ensure compliance and sustainable use of this chemical in various applications.
| Application Area | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Retardants | Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) is utilized in the production of flame-retardant materials. | Enhances fire resistance in various products, thus improving safety. |
| Paints and Coatings | Used to formulate high-performance industrial coatings. | Provides excellent durability and protective qualities. |
| Plastics Processing | Acts as a crosslinking agent in various plastics. | Improves mechanical properties and thermal stability of plastics. |
| Adhesives | Incorporated in adhesives for enhanced performance and bonding. | Increases adhesion strength and resistance to environmental conditions. |
| Textiles | Used in textile treatments to provide flame-resistant properties. | Ensures safety and compliance with fire safety standards. |
Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) has gained significant attention due to its versatility in various chemical applications, particularly in the production of flame retardants and other specialty chemicals. However, its environmental impact and safety considerations cannot be overlooked. Studies have shown that TBPA can persist in the environment, and its potential to bioaccumulate raises concerns about its long-term effects on ecosystems. When released into water bodies, it can affect aquatic organisms, disrupting their growth and reproductive systems, thereby posing a risk to biodiversity.
Moreover, the handling and use of Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride necessitate strict safety protocols. Its chemical properties can lead to irritations and allergic reactions in humans, necessitating the use of personal protective equipment during production and application. Ensuring safe disposal methods is equally important to prevent contamination of soil and water sources. As regulatory agencies continue to evaluate the implications of chemicals like TBPA, manufacturers must adopt sustainable practices and innovate safer alternatives to mitigate adverse environmental impacts while meeting market demands.
Tetrabromo phthalic anhydride (TBPA) is gaining traction in various chemical applications due to its unique properties, notably its flame-retardant capabilities and stability under high temperature. As sustainability becomes a focal point in industrial practices, the demand for TBPA is growing, particularly in the development of eco-friendly materials. Future trends indicate an increase in its application across a spectrum of industries, from electronics to construction, where its effectiveness can help meet regulatory standards for fire safety.
Additionally, innovations in TBPA formulations are paving the way for enhanced performance in diverse environments. Researchers are exploring modified versions of TBPA that maintain its flame-retardant qualities while reducing environmental impact. Emerging applications in renewable energy, particularly in the production of advanced composites for wind and solar energy technologies, showcase TBPA's versatility and potential to support sustainable practices.
Tips: When considering the use of TBPA, it's crucial to stay informed about the latest research on its formulations and applications. Collaborating with chemical safety experts can also ensure compliance with industry regulations, making the transition to TBPA-based solutions more seamless.