- Abemaciclib Intermediates
- Larotrectinib Intermediate
- Ivacaftor Intermediates
- AZD-9574 Intermediate
- AZD-5305 Intermediate
- Delafloxacin Intermediates
- Ponatinib Intermediates
- Baloxavir Intermediates
- Lisapram Intermediates
- Suzetrigine(VX548) Intermediate
- Resmetirol GL3196 Intermediate
- Dotinod Intermediates
- Other Intermediates
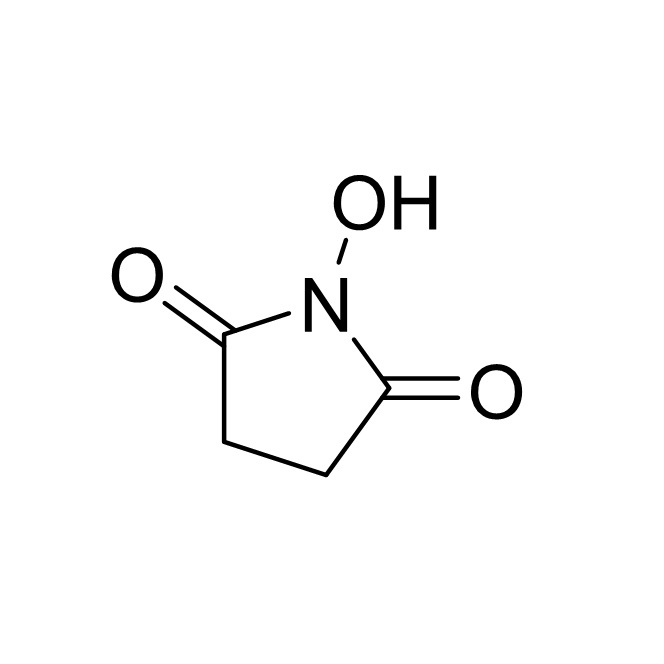
N-Hydroxysuccinimide CAS:6066-82-6
ZhonghanProduct Overview
N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) is a compound widely used in organic chemistry and biochemistry.
ZhonghanStructural formula
Molecular formula |
C4H5NO3 |
Molecular weight |
115.09 |
Melting point |
95-98 °C (lit.) |
Boiling point |
215.33°C (rough estimate) |
Density |
1.4769 (rough estimate) |
Form |
liquid or solid |
Color |
Transparent yellow-brown to brown |
Refractive index |
1.4080 (estimate) |
Storage conditions |
Store at +2°C to +8°C. |
Solubility |
soluble in DMSO (solubility in water is), methanol (trace amount) |
Acidity coefficient |
7.81±0.20 (Predicted) |
Water solubility |
SOLUBLE |
Vapor pressure |
0Pa at 25℃ |
ZhonghanPhysical properties
1. Appearance: It is white crystalline powder with stable properties, easy to store and use;
2. Melting point: 95-98℃, physical state changes will occur when reaching this temperature range;
3. Solubility: It is easily soluble in polar organic solvents such as water, alcohol, and acetone. Its good solubility enables it to play a role in a variety of reaction systems.
ZhonghanApplication Areas
1. Bioconjugation reaction: NHS is a commonly used activation reagent in bioconjugation chemistry. It is often used in combination with carbodiimide (such as EDC) to activate carboxyl groups and promote the covalent connection between biological molecules such as proteins, peptides, antibodies and other molecules (such as fluorescent markers, solid phase carriers, etc.). It is widely used in biosensors, immunoassays, targeted drug delivery and other fields;
2. Peptide synthesis: In the process of peptide chemical synthesis, NHS participates in the reaction as a condensation agent, which can effectively promote the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, improve the synthesis efficiency and purity of peptides, and is crucial to the artificial synthesis of complex peptides and proteins;
3. Drug research and development: used to synthesize compounds with specific biological activities as drug precursors or intermediates, providing structurally diverse raw materials for the research and development of new drugs, and helping to develop more efficient and less toxic therapeutic drugs.

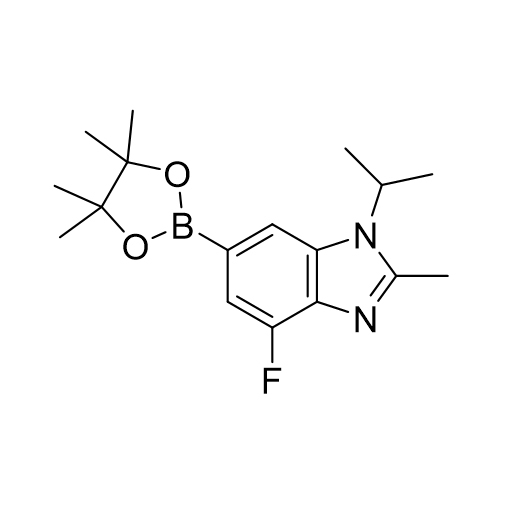
![6-Bromo-4-fluoro-1-isopropyl-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole CAS:1231930-33-8](/source/9e9faa51f944bc7ac934c145f661fec3/cas1231930-33-8.jpg)
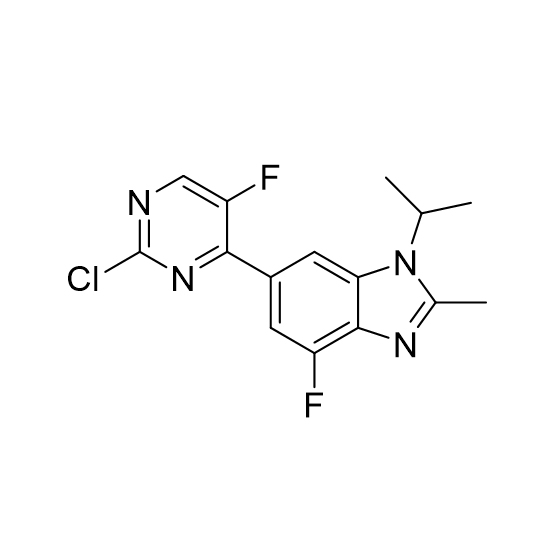
![5-Hydroxypyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine CAS:29274-22-4](https://ecdn6.globalso.com/upload/p/3069/image_product/2025-02/cas29274-22-4.jpg)
![5-Chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine CAS:29274-24-6](/source/2d2e4c8649a6444c8114fbceac0e361d/cas29274-24-6.jpg)
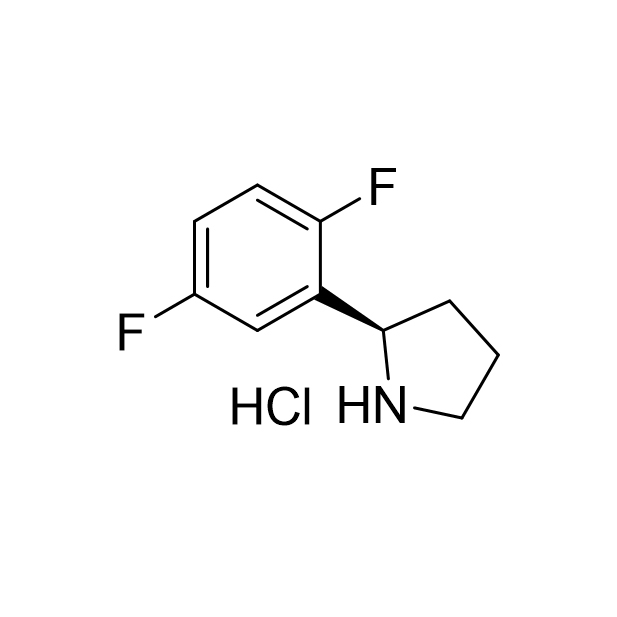
![5-Chloro-3-nitropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyriMidine CAS:1363380-51-1](/source/c735e97d9d2434baa533916048357d17/cas1363380-51-1.jpg)